What Are The Parts of the Brain?
In order to understand how the mind works, it is important to have a basic understanding of the different parts of the brain and its functions. Some people believe that the brain gives rise to consciousness, while still others believe it to be a transmitter that gives and receives information from consciousness. Either way, we all know that our individual, human bodies would not survive without the brain!
The Brain Consists of Three Major Components: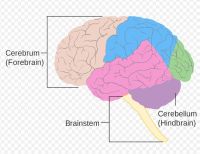
- Cerebrum
- Cerebellum
- Brain Stem
The Cerebrum:
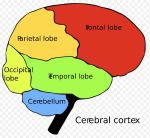
The Cerebrum is the very largest part of the human brain. The Cerebrum is divided into four sections: the Frontal Lobe, the Temporal Lobe, the Parietal Lobe, and the Occipital Lobe. The Cerebrum is covered by the Neo-Cortex (also known as the Cerebral Cortex.) This is a thin sheet of neural tissue. The Cerebrum is also called the Forebrain.
What Are Neurons?
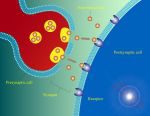
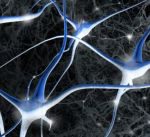
Neurons are the nerve cells (or brain cells) that transmit electrochemical signals throughout the entire Central 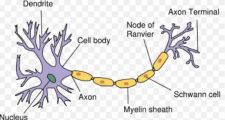 Nervous System. The average brain contains approximately over 100 billion neurons and even many more glial cells. Glial cells support and protect the neurons.
Nervous System. The average brain contains approximately over 100 billion neurons and even many more glial cells. Glial cells support and protect the neurons.
Neurons connect together with many other neurons, passing millions of signals back and forth and forming trillions of Synaptic Connections. Synaptic Connections are when the neurons communicate with one another, passing information from one to the other.
What Is The Cerebral Cortex?
The Cerebral Cortex is the outer layer of the brain that consists of gray matter. This is where sensory data is analyzed and memory function takes place. It is responsible for the ability to learn new information, form thought and make decisions.
The Cerebrum is also divided into the left and right side of the brain. The right side of the brain controls the left side of the body and the left side of the brain controls the right side of the body. These two hemispheres are linked together by a bundle of nerve fibers called the Corpus Callosum and divided by longitudinal fissure.
The Left Side and the Right Side: 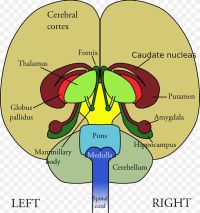
The left side of the brain is noted for being responsible for logical reasoning such as analysis and abstract reasoning. It plays a vital part in language, including comprehension. Mathematical skills, speech, writing, and comprehension are commonly thought to be predominately carried out through the left side of the brain.
The right side is what gives us spatial abilities. Memory is stored here by way of auditory, visual and spatial proficiencies. Creativity is thought to be paramount on the right side of the brain by way of creative, artistic and musical abilities. Messages are relayed back and forth between these two hemispheres by axons which transfer and relay important messages.
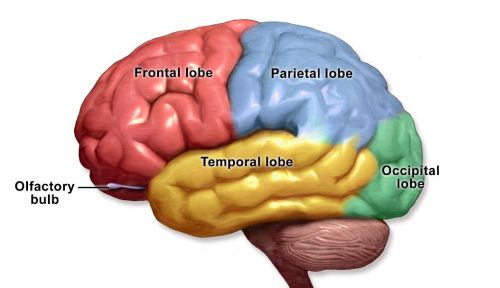
The Four Lobes:
The Frontal Lobe is where the higher functions of human intellect occur. This is the part of our brain that gives us intelligence and makes us self-aware. It is also the part of the brain that gives us the ability to judge, plan, reason and problem solve. This is where we pay attention and are able to form abstract thought and inhibitions.
The Parietal Lobe is responsible for sensory input, language into words, and comprehending signals from what we see, hear, sense and remember. It consists of the Sensory Cortex and the Motor Cortex.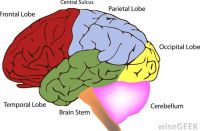
The Sensory Cortex is the front of the Parietal Lobe and it is responsible for us being aware of the position of body parts, as well as the ability to sense touch, pain, and pressure. Information is received and relayed from the Spinal Cord to the Sensory Cortex.
The Motor Cortex is in the top, the middle part of the Parietal Lobe. This is where we monitor and control our movements.
The Temporal Lobe is the part of the brain that is located in the Cerebral Hemisphere. It gives us the ability to form visual and auditory memories, as well as speech and hearing. The Wernicke’s Area is found here and this is the part of the brain that helps us to formulate, understand and recognize speech. It is formed around the Auditory Cortex.
The Occipital Lobe is in the very back of the head. This is the part of the brain that interprets everything that we see. The Broca’s Area is found here, which controls facial neurons and the ability to understand speech and language.
The Cerebellum:
The Cerebellum is called the “Little Brain” and this is what gives us motor control. It is responsible for essential functions such as how we can maintain our posture and balance, as well as the ability to coordinate movement. It also plays a role in our ability to pay attention.
The Basal Ganglia is the part of the brain that works with the Cerebellum. It coordinates very fine movements, such as those we perform with our fingertips.
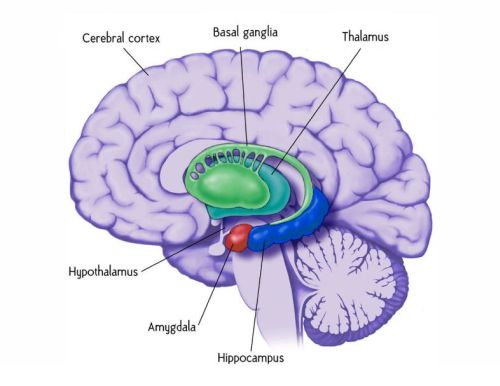
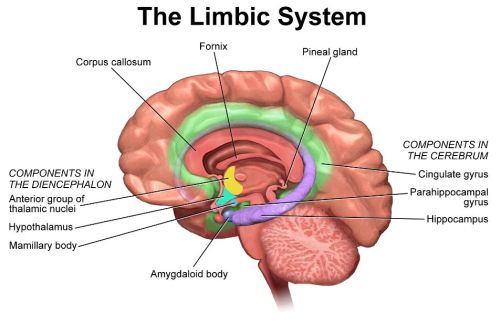
The Limbic System:
The Limbic System is the relay station for emotions. It consists of the Amygdala, the Hippocampus, and the Hypothalamus. It is also responsible for some learning, memory and hormonal responses. Olfactory pathways and biological rhythms can be found here as well.
Amygdala – this is the part of the brain responsible for the emotion of fear. It responds to emotions and helps cement emotions into memories. This is where the Fight or Flight response takes place.
The Hippocampus is where learning memory is stored. It can analyze, remember spatial relationships and take temporary memories and transform them into more permanent ones.
The Hypothalamus is the part of the brain that controls our mood. It is also what helps us to know when we are hungry, thirsty, too hot or too cold. It regulates hormones and governs the endocrine system and emotions, especially the “reward” emotions.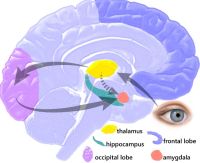
The Pituitary Gland controls our body temperature, and important functions such as feeding, drinking, sexual response, aggression, and pleasure. It contributes to muscle growth and it responds to stress from the environment. This is known as the Master Endocrine and it connects to the Hypothalamus.
The Thalamus is the center of the brain where our attention span is governed. It senses pain and is a relay station for messages between the cerebral cortex and the lower parts of the brain. It also relays information from the brain stem to the spinal cord. It is responsible for attention, alertness, and memory.
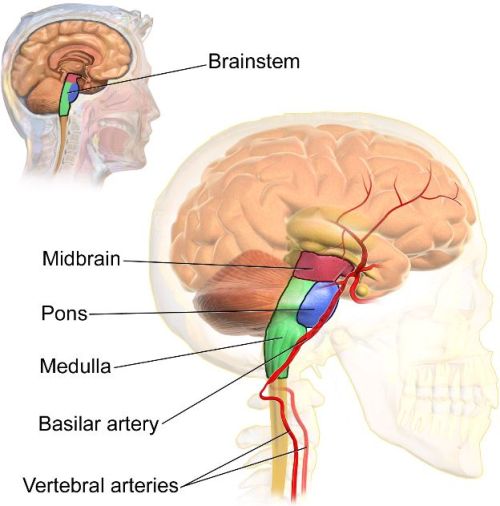
The Brain Stem:
The Brain Stem is responsible for our most basic and vital functions such as heartbeat, blood pressure, and breathing. It is the most primitive, simplest part of the brain, also known as the “Reptile” brain. It consists of the Midbrain, the Pons and the Medulla.
The Midbrain controls our body movements, hearing, vision and the transfer of messages from the cerebral cortex all the way down to the brain stem. It allows for voluntary motor function.
The Pons is located in the hindbrain. It links the cerebellum which helps to direct arousal, respiration, posture, and movement. The Pons interprets information and helps us to get into a sleep state. It analyzes sensory information and motor control.
The Medulla Oblongata maintains extremely vital functions. This is the most primitive area responsible for keeping us alive, heart pumping and lungs breathing.
The Pineal Gland is the tiny part of the brain responsible for our internal clock and circadian sleep rhythms. This is what is commonly referred to as the “Third Eye” in certain cultures.
The Reticular Formation is also found in the Brain Stem. This is the part of the brain that controls arousal.
And finally, the Spinal Cord is the pathway from the brain down our back and it is the pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from the brain. It controls simple reflexes and other important functions.
Find out the latest research by clicking here and how to use it to eliminate stress in your life.
I hope that you will find this to be a valuable reference that will help you to better understand the role the brain plays in the study of mind. I don’t know about you, but for me, the brain INSPIRES me!! How does the brain inspire you? As always, your comments are welcomed and appreciated!